mirror of
https://github.com/KazooTTT/kazoottt-blog.git
synced 2025-06-23 10:41:31 +08:00
docs: update
This commit is contained in:
58
src/content/post/编程/前端/css/链接样式需要遵循LVHA顺序的原因.md
Normal file
58
src/content/post/编程/前端/css/链接样式需要遵循LVHA顺序的原因.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,58 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: CSS | 链接样式需要遵循LVHA顺序的原因
|
||||
date: 2021-07-23
|
||||
author: KazooTTT
|
||||
tags:
|
||||
- CSS
|
||||
- 学习笔记
|
||||
- 《深入解析CSS》
|
||||
- 前端
|
||||
slug: reasons-why-link-styles-need-to-follow-the-lvha-order
|
||||
published: true
|
||||
description: 在CSS中,链接的伪类选择器(:link, :visited, :hover, :active)遵循LVHA顺序的原因是为了确保样式正确应用。由于这些伪类的优先级相同,后定义的样式会覆盖先前的样式。因此,为了防止样式冲突,应按照LVHA顺序定义这些伪类,即先定义:link,然后是:visited,接着是:hover,最后是:active。这样的顺序确保了链接在不同状态下的样式能够正确显示,例如在鼠标悬停或点击时。
|
||||
NotionID-notionnext: https://kazoottt.notion.site/d4aa37afdc8147d89869d67ebb5b4e7c
|
||||
category: 编程-前端-css
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
# 链接样式需要遵循 LVHA 顺序的原因
|
||||
|
||||
《深入解析 CSS》中有这样一句话
|
||||
|
||||
> 伪类选择器(如:hover)和属性选择器(如[type="input"])与一个类选择器的优先级相同。通用选择器(*)和组合器(>、+、~)对优先级没有影响。
|
||||
|
||||
也就是说对于以下四个伪类,没有优先级之分。
|
||||
|
||||
如果某一个链接同时处于两个或者以上的状态,并且状态对应的样式产生了冲突,后出现的样式就会覆盖掉前面的样式。
|
||||
|
||||
```css
|
||||
a:link {
|
||||
color: blue;
|
||||
text-decoration: none;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
a:visited {
|
||||
color: purple;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
a:hover {
|
||||
text-decoration: underline;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
a:active {
|
||||
color: red;
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**那么为什么需要遵循 LVHA(link visited\hover active)顺序呢**?分析如下:
|
||||
|
||||
:link 这两个伪类是固定的状态(:link 是最原始的状态,:visited 是被点击过后就产生,这两个状态产生之后是一直存在的)
|
||||
|
||||
:hover :active 不是固定的,需要鼠标去触发,并且触发完毕之后会消失。
|
||||
|
||||
所以:link 作为最原始的状态,它的样式应该放在最前面,:visited 紧随其后。
|
||||
|
||||
而对于:hover 以及:active,设想一下如果:active 在:hover 之前,鼠标放到链接上去的时候,直接显示:hover 的颜色。点击链接的时候,由于:hover 在:active 下面,会覆盖 active 的颜色,这并不符合我们的需求,所以:active 应该在:hover 之后。
|
||||
|
||||
综上,由于伪类的优先级一致,后出现的样式会覆盖前面的样式,所以链接的样式应该遵循 LVHA 顺序
|
||||
|
||||
(方便记忆:love hate—> link visited hover active)
|
||||
48
src/content/post/编程/前端/node/node path模块相关操作.md
Normal file
48
src/content/post/编程/前端/node/node path模块相关操作.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,48 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: node | path模块相关操作
|
||||
subtitle: 记录一些常用用法和区别,以及犯的错。
|
||||
date: 2022-10-24
|
||||
author: KazooTTT
|
||||
tags:
|
||||
- path
|
||||
- 前端
|
||||
- node
|
||||
slug: node-path-module-related-operations
|
||||
published: true
|
||||
description: >-
|
||||
本文介绍了Node.js中path模块的常用操作,包括__dirname与process.cwd()的区别,以及path.join()和path.resolve()的差异。特别指出,__dirname和process.cwd()在使用时需注意其返回的路径差异,以免导致静态资源加载失败。同时,path.join()用于连接路径,而path.resolve()则解析为绝对路径。这些知识点对于正确配置和处理文件路径至关重要。
|
||||
category: 编程-前端-node
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
# Path 相关操作
|
||||
|
||||
path 是 node 的一个常用模块。
|
||||
|
||||
## 常用用法
|
||||
|
||||
TODO
|
||||
|
||||
## 区别
|
||||
|
||||
1. \_\_dirname 和 process.cwd()的区别
|
||||
|
||||
[node.js - What's the difference between process.cwd() vs \_\_dirname? - Stack Overflow](https://stackoverflow.com/questions/9874382/whats-the-difference-between-process-cwd-vs-dirname)
|
||||
|
||||
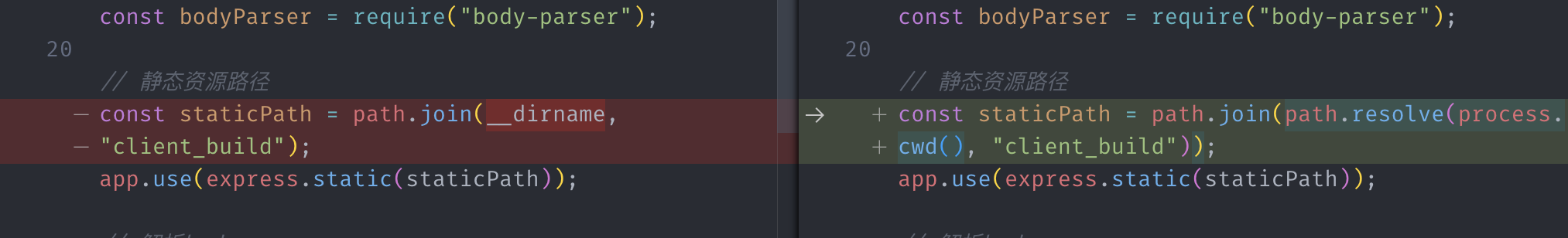
|
||||
|
||||
此段代码意在配置静态资源路径,由于错误使用\_\_dirname,导致静态资源加载失败。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
xxx/server_build/client_build // 前者返回
|
||||
xxx/client_build // 后者返回
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
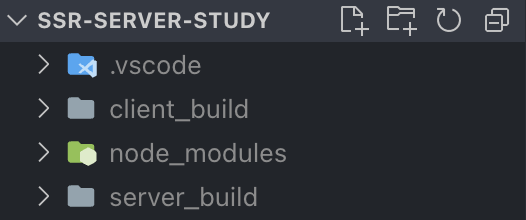
|
||||
|
||||
而目录结构为上图,express-对应 server 打包在 server_bulid,需要加载的 client scripts 在 client_buiild,为同级目录,所以第一张图右边的写法才能正确配置静态资源路径。
|
||||
|
||||
2. path.join()和 path.resolve()的区别
|
||||
|
||||
连接路径
|
||||
|
||||
path.resolve() ==> 解析为绝对路径
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,18 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: AMD
|
||||
date: 2023-09-27
|
||||
author: KazooTTT
|
||||
tags:
|
||||
- node
|
||||
- amd
|
||||
published: true
|
||||
slug: amd
|
||||
description: AMD, or Asynchronous Module Definition, is a JavaScript specification for defining modules where the module and its dependencies can be asynchronously loaded. This is particularly useful for web applications where scripts can be loaded in parallel, improving performance and efficiency.
|
||||
category: 编程-前端-node
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
# AMD
|
||||
|
||||
[[CommonJS简介]]
|
||||
|
||||
## 什么是 AMD
|
||||
84
src/content/post/编程/前端/node/npm和npx的区别.md
Normal file
84
src/content/post/编程/前端/node/npm和npx的区别.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,84 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: npm和npx的区别
|
||||
date: 2023-09-06
|
||||
author: KazooTTT
|
||||
finished: false
|
||||
published: true
|
||||
slug: difference-between-npm-and-npx
|
||||
description: >-
|
||||
本文详细介绍了npm和npx的区别,包括它们的定义、使用场景和具体用法。npm是Node.js的默认包管理器,用于安装、卸载和升级包,而npx是一个命令行工具,允许用户直接运行项目中的二进制文件,无需全局安装。文章通过实例说明了两者在实际开发中的应用,如使用npm安装ant
|
||||
design,以及使用npx创建nextjs项目。
|
||||
category: 编程-前端-node
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
# Npm和npx的区别
|
||||
|
||||
在日常的开发中,经常会使用这两个指令。
|
||||
|
||||
例如使用 npm 引入 ant design
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
npm install antd
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
[Create Next App | Next.js (nextjs.org)](https://nextjs.org/docs/api-reference/create-next-app) 中运行使用 npx 来创建 nextjs 项目
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
npx create-next-app@latest
|
||||
# or
|
||||
yarn create next-app
|
||||
# or
|
||||
pnpm create next-app
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
本文将从两者的定义、区别、使用场景这三个部分进行阐述。
|
||||
|
||||
## Npm 和 Npx 的定义
|
||||
|
||||
开宗明义,首先需要弄清楚 npm 和 npx 的定义以及它们具体是用来做什么的。
|
||||
|
||||
### Npm 的定义
|
||||
|
||||
我从书籍或者网站中找了一些关于 npm 的定义。例如在《JavaScript 高级程序设计 4th》,作者对 npm 的定义如下:
|
||||
|
||||
> npm,即 Node 包管理器(Node Package Manager),是 Node.js 运行时默认的包管理器。在 npm 仓库中发布的第三方包可以指定为项目依赖,并通过命令行本地安装。npm 仓库包含服务端和客户端 JavaScript 库。
|
||||
> npm 是为在服务器上使用而设计的,服务器对依赖大小并不敏感。在安装包时,npm 使用嵌套依赖树解析所有项目依赖,每个项目依赖都会安装自己的依赖。这意味着如果项目依赖三个包 A、B 和 C,而这三个包又都依赖不同版本的 D,则 npm 会安装包 D 的三个版本。
|
||||
|
||||
在 freecodecamp 的技术分享博客([什么是 npm —— 写给初学者的编程教程 (freecodecamp.org)](https://www.freecodecamp.org/chinese/news/what-is-npm-a-node-package-manager-tutorial-for-beginners/))中,作者对 npm 的定义如下:
|
||||
|
||||
> npm(“Node 包管理器”)是 JavaScript 运行时 Node.js 的默认程序包管理器。
|
||||
> npm 由两个主要部分组成:
|
||||
>
|
||||
> 1. 用于发布和下载程序包的 CLI(命令行界面)工具
|
||||
> 2. 托管 JavaScript 程序包的 [在线存储库](https://www.npmjs.com/)
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
也就是说 npm 的本质是包管理器。
|
||||
|
||||
如何管理包?
|
||||
|
||||
对于本地,使用 CLI 进行包的安装,卸载、升级
|
||||
对于 npm 存储库,使用 CLI 进行将包发布到存储库中
|
||||
包从何而来?
|
||||
|
||||
npm 存储库 <=== 他人使用 CLI 进行将包发布到存储库中
|
||||
|
||||
很显然在本文开头 npm 命令其实代指的命令行工具,而不是包管理器这个概念本身。
|
||||
|
||||
综上,提到 npm 的时候可能有两个定义,一个是包管理器(本身的定义),一个是包管理器对应的命令行工具(使用过程中代指的定义)。
|
||||
|
||||
### Npx 的定义
|
||||
|
||||
在[什么是 npm —— 写给初学者的编程教程 (freecodecamp.org)](https://www.freecodecamp.org/chinese/news/what-is-npm-a-node-package-manager-tutorial-for-beginners/) 中提到
|
||||
|
||||
> 最新引入的 [npx](https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/npm-vs-npx-whats-the-difference/) 使我们可以像在全局安装程序一样运行这些 `node_modules` 项目作用域命令,方法是在其前面加上 `npx ...`(即`npx prettier --write ** / *。ts`)。
|
||||
|
||||
## 用法
|
||||
|
||||
[npx 使用教程 - 阮一峰的网络日志 (ruanyifeng.com)](https://www.ruanyifeng.com/blog/2019/02/npx.html)
|
||||
|
||||
如果要运行项目中的某些二进制文件,以前只能使用 路径/bin 文件 来执行
|
||||
但是使用 npx 就可以直接运行了
|
||||
|
||||
> npx 的原理很简单,就是运行的时候,会到`node_modules/.bin`路径和环境变量`$PATH`里面,检查命令是否存在。由于 npx 会检查环境变量`$PATH`,所以系统命令也可以调用。
|
||||
68
src/content/post/编程/前端/node/npm换源.md
Normal file
68
src/content/post/编程/前端/node/npm换源.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,68 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: npm换源
|
||||
date: 2024-02-07
|
||||
author: KazooTTT
|
||||
tags:
|
||||
- npm
|
||||
- node
|
||||
published: true
|
||||
slug: npm-registry
|
||||
description: >-
|
||||
本文介绍了如何查看、更换和取消Node.js包管理工具(npm, yarn,
|
||||
pnpm)的源地址,以及如何使用yrm工具快速切换不同的npm源。通过执行特定的命令,用户可以轻松地管理这些工具的源设置,从而优化包的下载速度和开发效率。
|
||||
category: 编程-前端-node
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
# 查看源
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
npm config get registry
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
yarn config get registry
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
pnpm config get registry
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
# 换源
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
npm config set registry https://registry.npmmirror.com
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
yarn config set registry https://registry.npmmirror.com
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
pnpm config set registry https://registry.npmmirror.com
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
# 取消换源
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
npm config delete registry
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
yarn config delete registry
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
pnpm config delete registry
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
# 工具
|
||||
|
||||
[GitHub - i5ting/yrm: YARN registry manager, fast switch between different registries: npm, cnpm, nj, taobao](https://github.com/i5ting/yrm)
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
npm install -g yrm
|
||||
|
||||
yrm ls
|
||||
|
||||
yrm use [name]
|
||||
```
|
||||
48
src/content/post/编程/后端/python/flask-jwt.md
Normal file
48
src/content/post/编程/后端/python/flask-jwt.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,48 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
slug: flask-jwt
|
||||
published: true
|
||||
description: 本文对比了几个Flask可用的JWT库,包括flask-jwt-extended、Flask-JWT和jwt,根据PyPI下载量和Star量,选择使用最广泛的flask-jwt-extended。文章介绍了在父页面通过iframe嵌入子页面时,如何在子页面中验证和使用JWT token,包括页面级别和接口级别的token验证。同时,提供了安装flask-jwt-extended的命令,并建议参考官方文档进行详细配置。
|
||||
category: 编程-后端-python
|
||||
title: flask-jwt
|
||||
date: 2024-09-10
|
||||
author: KazooTTT
|
||||
type: Post
|
||||
status: Published
|
||||
tags:
|
||||
finished: false
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
# Flask-jwt
|
||||
|
||||
## Flask可用库的对比
|
||||
|
||||
flask-jwt-extended的使用量是最多的,为了后期更好地项目维护,还是选择第一个来使用。
|
||||
|
||||
## 使用flask-jwt-extended
|
||||
|
||||
场景:
|
||||
|
||||
父页面 + iframe嵌入子页面,嵌入的时候url带上token。
|
||||
|
||||
在子页面需要做的事情:
|
||||
|
||||
1. 页面级别:每个页面都需要验证token是否有效。
|
||||
2. 接口级别:每个接口都需要验证token是否有效。
|
||||
|
||||
### 对于页面
|
||||
|
||||
父页面使用iframe嵌入子页面的时候,url带上token。因此在子页面加载的时候需要处理url以获取token,然后把它存储在localStorage中。在后续接口调用中都需要把token带上,以便于接口的鉴权。
|
||||
|
||||
### 对于接口
|
||||
|
||||
实现一个装饰器,用于校验token。
|
||||
|
||||
## 具体过程
|
||||
|
||||
[参考文档](https://flask-jwt-extended.readthedocs.io/en/stable/basic_usage.html)
|
||||
|
||||
1. 安装`flask-jwt-extended`
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
pip install flask-jwt-extended
|
||||
```
|
||||
62
src/content/post/编程/后端/python/python之禅.md
Normal file
62
src/content/post/编程/后端/python/python之禅.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,62 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: python之禅
|
||||
date: 2024-03-04
|
||||
author: KazooTTT
|
||||
tags:
|
||||
- python
|
||||
finished: false
|
||||
published: true
|
||||
slug: the-zen-of-python
|
||||
description: >-
|
||||
The Zen of Python, written by Tim Peters, is a collection of guiding
|
||||
principles for writing computer programs that are both beautiful and
|
||||
effective. It emphasizes the importance of simplicity, readability, and
|
||||
explicitness in coding. The text advocates for avoiding complexity and
|
||||
ambiguity, and encourages the use of namespaces. It also highlights the value
|
||||
of practicality over theoretical purity, and stresses that errors should not
|
||||
be ignored. Overall, the Zen of Python promotes clarity and elegance in
|
||||
programming practices.
|
||||
category: 编程-后端-python
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
# Python之禅
|
||||
|
||||
> The Zen of Python, by Tim Peters
|
||||
>
|
||||
> Beautiful is better than ugly.
|
||||
>
|
||||
> Explicit is better than implicit.
|
||||
>
|
||||
> Simple is better than complex.
|
||||
>
|
||||
> Complex is better than complicated.
|
||||
>
|
||||
> Flat is better than nested.
|
||||
>
|
||||
> Sparse is better than dense.
|
||||
>
|
||||
> Readability counts.
|
||||
>
|
||||
> Special cases aren't special enough to break the rules.
|
||||
>
|
||||
> Although practicality beats purity.
|
||||
>
|
||||
> Errors should never pass silently.
|
||||
>
|
||||
> Unless explicitly silenced.
|
||||
>
|
||||
> In the face of ambiguity, refuse the temptation to guess.
|
||||
>
|
||||
> There should be one-- and preferably only one --obvious way to do it.
|
||||
>
|
||||
> Although that way may not be obvious at first unless you're Dutch.
|
||||
>
|
||||
> Now is better than never.
|
||||
>
|
||||
> Although never is often better than _right_ now.
|
||||
>
|
||||
> If the implementation is hard to explain, it's a bad idea.
|
||||
>
|
||||
> If the implementation is easy to explain, it may be a good idea.
|
||||
>
|
||||
> Namespaces are one honking great idea -- let's do more of those!
|
||||
51
src/content/post/编程/后端/python/python常用的命令备忘.md
Normal file
51
src/content/post/编程/后端/python/python常用的命令备忘.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,51 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: python常用的命令备忘
|
||||
date: 2024-03-27T00:00:00.000Z
|
||||
author: KazooTTT
|
||||
tags: []
|
||||
finished: false
|
||||
published: true
|
||||
slug: commonly-used-command-memos-in-python
|
||||
description: >-
|
||||
本文介绍了如何在当前环境下导出最小依赖以及配置Python包管理工具pip的镜像源。首先,通过安装`pipreqs`工具并使用命令`pipreqs ./
|
||||
--encoding=utf8`在项目根目录导出依赖。其次,讲解了如何在Windows系统中通过修改`pip.ini`文件或使用命令行配置pip的镜像源,包括设置镜像源地址、取消配置以及查看当前配置的方法。
|
||||
category: 编程-后端-python
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
# Python常用的命令备忘
|
||||
|
||||
## 导出当前环境下的最小依赖
|
||||
|
||||
首先安装包
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
pip install pipreqs
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
然后在环境根目录导出
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
pipreqs ./ --encoding=utf8
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 镜像源配置
|
||||
|
||||
在windows中,搜索pip.ini,去修改
|
||||
|
||||
或者使用命令行来配置
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
pip config set global.index-url https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
取消配置
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
pip config unset global.index-url
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
读取当前的配置:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
pip config get global.index-url
|
||||
```
|
||||
109
src/content/post/编程/后端/python/管理python环境的方式.md
Normal file
109
src/content/post/编程/后端/python/管理python环境的方式.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,109 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: 管理python环境的方式
|
||||
date: 2023-12-05
|
||||
author: KazooTTT
|
||||
tags:
|
||||
- python
|
||||
- 环境管理
|
||||
- pyenv
|
||||
- poetry
|
||||
- conda
|
||||
published: true
|
||||
slug: managing-the-python-environment
|
||||
description: >-
|
||||
本文总结了管理Python环境的几种主流方式,包括venv、virtualenv、conda、pipenv和poetry等。虚拟环境能够为不同的项目提供独立的Python版本和依赖库,避免了全局解释器带来的切换和维护问题。文章还介绍了作者个人常用的环境管理工具:pyenv用于Python版本管理,poetry和virtualenv用于依赖管理。此外,还简要说明了conda的使用注意事项,建议避免与pip混用,并了解import优先级。
|
||||
category: 编程-后端-python
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
# 管理python环境的方式
|
||||
|
||||
最近又有写 python 的需求了,上一次写还是几年前写圣纳百川爬虫的时候,因此很多事情记不太清楚了。
|
||||
|
||||
本文主要来疏离总结一下管理 python 环境的方式,以及它们的适用场景。
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
## 主流的方案
|
||||
|
||||
对于不同的项目,它们会用到不同的 python 版本,以及不同的依赖库和版本。如果只使用全局解释器,那么切换和维护起来会非常的麻烦且容易出错。面对这样的场景,虚拟环境是更优的选择。
|
||||
|
||||
在官方文档中提到:[venv --- 创建虚拟环境 — Python 3.12.0 文档](https://docs.python.org/zh-cn/3/library/venv.html)
|
||||
|
||||
> `venv` 模块支持创建轻量的“虚拟环境”,每个虚拟环境将拥有它们自己独立的安装在其 [`site`](https://docs.python.org/zh-cn/3/library/site.html#module-site "site: Module responsible for site-specific configuration.") 目录中的 Python 软件包集合。虚拟环境是在现有的 Python 安装版基础之上创建的,这被称为虚拟环境的“基础”Python,并且还可选择与基础环境中的软件包隔离开来,这样只有在虚拟环境中显式安装的软件包才是可用的。
|
||||
|
||||
那么虚拟环境的管理具体有哪些呢?
|
||||
|
||||
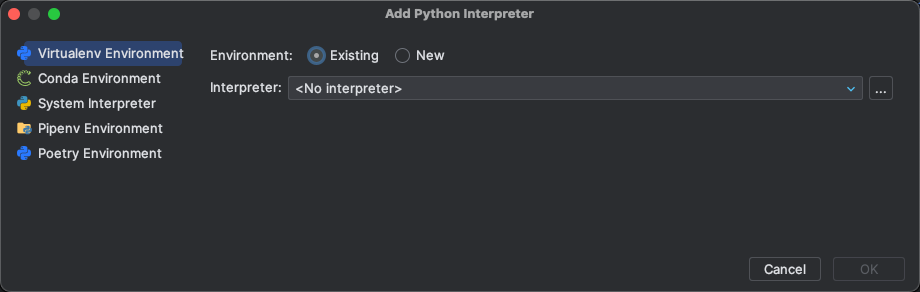
|
||||
我们从 pycharm 提供的解释器选项中能看出一二,pycharm 这里提供的都是比较主流的虚拟环境管理了。
|
||||
|
||||
1. venv(官方内置的模块)
|
||||
2. virtualenv
|
||||
3. conda
|
||||
4. pipenv
|
||||
5. poetry
|
||||
|
||||
这里不想分别对这些管理工作都做详细的介绍,只记录我自己最常用的组合。
|
||||
|
||||
我的需求有两类,第一类管理 python 的版本,第二类管理依赖的版本。
|
||||
|
||||
## 对于 Python 版本管理
|
||||
|
||||
使用 pyenv
|
||||
[GitHub - pyenv/pyenv: Simple Python version management](https://github.com/pyenv/pyenv)
|
||||
用来安装和切换 python 的版本
|
||||
|
||||
## 对于依赖管理
|
||||
|
||||
如果是我自己的项目,那么我会使用 poetry(因为操作比较像 npm,我更加熟悉)
|
||||
|
||||
如果是别人的项目且项目中不是使用 poetry 来管理的,那么我会使用 virtualenv 来管理。
|
||||
|
||||
### Poetry
|
||||
|
||||
[Basic usage | Documentation | Poetry - Python dependency management and packaging made easy](https://python-poetry.org/docs/basic-usage/)
|
||||
|
||||
如果是一个新的项目
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
poetry new poetry-demo
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
如果是一个已经存在的项目
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
poetry init
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
然后使用`poetry add 包名`安装依赖
|
||||
也可以指定版本,[Dependency specification | Documentation | Poetry - Python dependency management and packaging made easy](https://python-poetry.org/docs/dependency-specification/)
|
||||
|
||||
如果要导出 requirements 方便别人安装可以运行
|
||||
`poetry export -o requirements.txt`
|
||||
|
||||
### Virtualenv
|
||||
|
||||
[virtualenv](https://virtualenv.pypa.io/en/latest/)
|
||||
|
||||
创建虚拟环境
|
||||
``virtualenv env_name
|
||||
|
||||
激活
|
||||
如果是 linux
|
||||
`source env_name/bin/activate`
|
||||
如果是 windows
|
||||
`.\env_name\Scripts\activate`
|
||||
|
||||
当然如果你用的 IDE,它会帮你创建和关联
|
||||
|
||||
然后后面就是正常的 pip install xxx 之类的操作了。
|
||||
|
||||
### Conda
|
||||
|
||||
[请问大神们,pip install 和 conda install 有什么区别吗? - 知乎](https://www.zhihu.com/question/395145313/answer/2449421755)
|
||||
conda 用来作为虚拟环境管理的话,不建议 pip 和 conda 混用,需要了解一下 import 优先级。
|
||||
|
||||
如果都安装了某一个包,那么优先 import 的是 conda 安装的
|
||||
|
||||
如果之前用 pip 装的,运行`conda convert`转一下。
|
||||
|
||||
然后后面都用 conda 来安装,conda 找不到的包再用 pip 来装。
|
||||
57
src/content/post/编程/算法/记录/141.环形链表.md
Normal file
57
src/content/post/编程/算法/记录/141.环形链表.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,57 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: 141.环形链表
|
||||
date: 2023-09-12T00:00:00.000Z
|
||||
author: KazooTTT
|
||||
tags:
|
||||
- 算法
|
||||
- 链表
|
||||
- leetcode
|
||||
platform: leetcode
|
||||
number: 141
|
||||
url: 'https://leetcode.cn/problems/linked-list-cycle/'
|
||||
finished: true
|
||||
published: true
|
||||
slug: 141-ring-chained-tables
|
||||
description: >-
|
||||
该内容描述了一个用于检测链表中是否存在环的算法。算法通过使用两个指针,一个慢指针和一个快指针,在链表中移动。如果链表中存在环,快指针最终会追上慢指针;否则,快指针会先到达链表的末尾。算法首先检查链表的头节点是否为空或其下一个节点是否为空,如果是,则返回false,表示没有环。然后,算法进入一个循环,每次循环中慢指针前进一步,快指针前进两步。如果快指针变为null或其下一个节点为null,则返回false,表示没有环。如果循环中快指针与慢指针相遇,则返回true,表示链表中存在环。
|
||||
rinId: 58
|
||||
category: 编程-算法-记录
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
# 141.环形链表
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
/*
|
||||
* @lc app=leetcode.cn id=141 lang=typescript
|
||||
*
|
||||
* [141] 环形链表
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
// @lc code=start
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* Definition for singly-linked list.
|
||||
* class ListNode {
|
||||
* val: number
|
||||
* next: ListNode | null
|
||||
* constructor(val?: number, next?: ListNode | null) {
|
||||
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
|
||||
* this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next)
|
||||
* }
|
||||
* }
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
function hasCycle(head: ListNode | null): boolean {
|
||||
if (head === null || head.next === null) return false
|
||||
let slow = head
|
||||
let fast = head.next
|
||||
while (slow !== fast) {
|
||||
if (fast === null || fast.next === null) return false
|
||||
slow = slow.next
|
||||
fast = fast.next.next
|
||||
}
|
||||
return true
|
||||
}
|
||||
// @lc code=end
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
17
src/content/post/编程/算法/记录/142.环形链表-ii.md
Normal file
17
src/content/post/编程/算法/记录/142.环形链表-ii.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,17 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: 【leetcode】142.环形链表-ii
|
||||
date: 2023-09-13T00:00:00.000Z
|
||||
author: KazooTTT
|
||||
tags:
|
||||
- 算法
|
||||
platform: leetcode
|
||||
url: 'https://leetcode.cn/problems/linked-list-cycle-ii/description/'
|
||||
finished: true
|
||||
published: true
|
||||
slug: 142-ring-linked-tables-ii
|
||||
description: 题目“142.环形链表-ii”指的是一个关于数据结构中环形链表的问题,特别是针对环形链表中特定节点的查找或操作问题。
|
||||
rinId: 118
|
||||
category: 编程-算法-记录
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
# 142.环形链表-ii
|
||||
32
src/content/post/编程/算法/记录/2024-03-05 刷题.md
Normal file
32
src/content/post/编程/算法/记录/2024-03-05 刷题.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,32 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
description: >-
|
||||
内容中提到了两个编程问题及其相关注意事项。首先,对于“两数之和”问题,指出了在JavaScript代码中,如果`numberToIndexMap[targetNumber]`的值为0时,使用`!==
|
||||
undefined`进行判断可能会导致错误的结果,建议使用`in`操作符来检查对象属性是否存在。其次,提到了“删除有序数组中的重复项”问题,强调了需要原地删除重复元素,即不使用额外的空间。
|
||||
slug: 2024-03-05-brush-questions
|
||||
finished: true
|
||||
published: true
|
||||
date: '2024-07-11T02:17:53.454Z'
|
||||
rinId: 119
|
||||
category: 编程-算法-记录
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
# 2024-03-05 刷题
|
||||
|
||||
需要注意的是
|
||||
|
||||
[1. 两数之和](https://leetcode.cn/problems/two-sum/)
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
if (numberToIndexMap[targetNumber] !== undefined) {
|
||||
const targetNumberIndex = numberToIndexMap[targetNumber]
|
||||
return [targetNumberIndex, i]
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
这里的写法,如果`numberToIndexMap[targetNumber] = 0` 的话, if也会判断为false,所以不能这么写。
|
||||
|
||||
要么写成`numberToIndexMap[targetNumber] !== undefined`要么写成 `if (targetNumber in numberToIndexMap)`
|
||||
|
||||
[26. 删除有序数组中的重复项](https://leetcode.cn/problems/remove-duplicates-from-sorted-array/)
|
||||
|
||||
请你 **[原地](http://baike.baidu.com/item/%E5%8E%9F%E5%9C%B0%E7%AE%97%E6%B3%95)** 删除重复出现的元素
|
||||
68
src/content/post/编程/算法/记录/86.分隔链表.md
Normal file
68
src/content/post/编程/算法/记录/86.分隔链表.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,68 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: 【leetcode】86.分隔链表
|
||||
date: 2023-09-13T00:00:00.000Z
|
||||
author: KazooTTT
|
||||
tags:
|
||||
- 算法
|
||||
- 链表
|
||||
- leetcode
|
||||
- 待优化
|
||||
- todo
|
||||
platform: leetcode
|
||||
number: 86
|
||||
url: 'https://leetcode.cn/problems/partition-list/description/'
|
||||
finished: true
|
||||
published: true
|
||||
slug: 86-separated-chained-tables
|
||||
description: >-
|
||||
该内容描述了一个TypeScript函数`partition`,用于将一个单链表分割成两部分:一部分包含所有小于给定值x的节点,另一部分包含所有大于或等于x的节点。函数首先创建两个新的链表头节点`small`和`large`,分别用于存储小于x和大于等于x的节点。通过遍历原链表,将节点值小于x的节点添加到`small`链表,将节点值大于等于x的节点添加到`large`链表。最后,将`large`链表连接到`small`链表的尾部,并返回`small`链表的头节点。此方法在内存使用上还有优化空间。
|
||||
rinId: 59
|
||||
category: 编程-算法-记录
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
# 86.分隔链表
|
||||
|
||||
```typescript
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* Definition for singly-linked list.
|
||||
* class ListNode {
|
||||
* val: number
|
||||
* next: ListNode | null
|
||||
* constructor(val?: number, next?: ListNode | null) {
|
||||
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
|
||||
* this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next)
|
||||
* }
|
||||
* }
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
function partition(head: ListNode | null, x: number): ListNode | null {
|
||||
let small = new ListNode(-1),
|
||||
smallP = small,
|
||||
large = new ListNode(-1),
|
||||
largeP = large
|
||||
|
||||
while (head) {
|
||||
if (head.val < x) {
|
||||
smallP.next = {
|
||||
val: head.val,
|
||||
next: null,
|
||||
}
|
||||
smallP = smallP.next
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
largeP.next = {
|
||||
val: head.val,
|
||||
next: null,
|
||||
}
|
||||
largeP = largeP.next
|
||||
}
|
||||
head = head.next
|
||||
}
|
||||
largeP.next = null
|
||||
smallP.next = large.next
|
||||
return small.next
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
可以看出内存还有很大的优化空间
|
||||
28
src/content/post/编程/算法/记录/leetcode刷题 js + python.md
Normal file
28
src/content/post/编程/算法/记录/leetcode刷题 js + python.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,28 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
slug: leetcode-brush-up
|
||||
published: true
|
||||
description: >-
|
||||
2023年1月10日,记录了在LeetCode上的刷题情况。首先完成了“两数之和”问题,随后解决了“删除有序数组中的重复项”,虽然使用的方法简单但性能较差。最后,解决了“移除元素”问题。每个问题都附有相关的提交链接和截图,以便记录和回顾。
|
||||
finished: true
|
||||
date: '2024-07-11T02:17:53.454Z'
|
||||
rinId: 120
|
||||
category: 编程-算法-记录
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
# Leetcode刷题
|
||||
|
||||
2023-01-10
|
||||
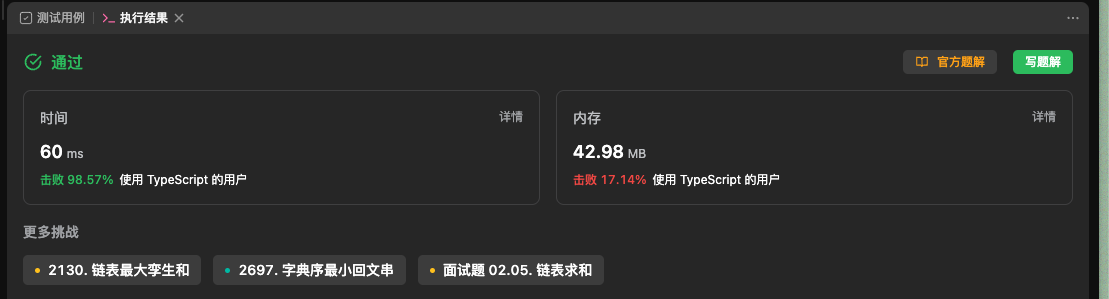
[1. 两数之和 - 力扣(LeetCode)](https://leetcode.cn/problems/two-sum/submissions/394403223/)
|
||||
|
||||
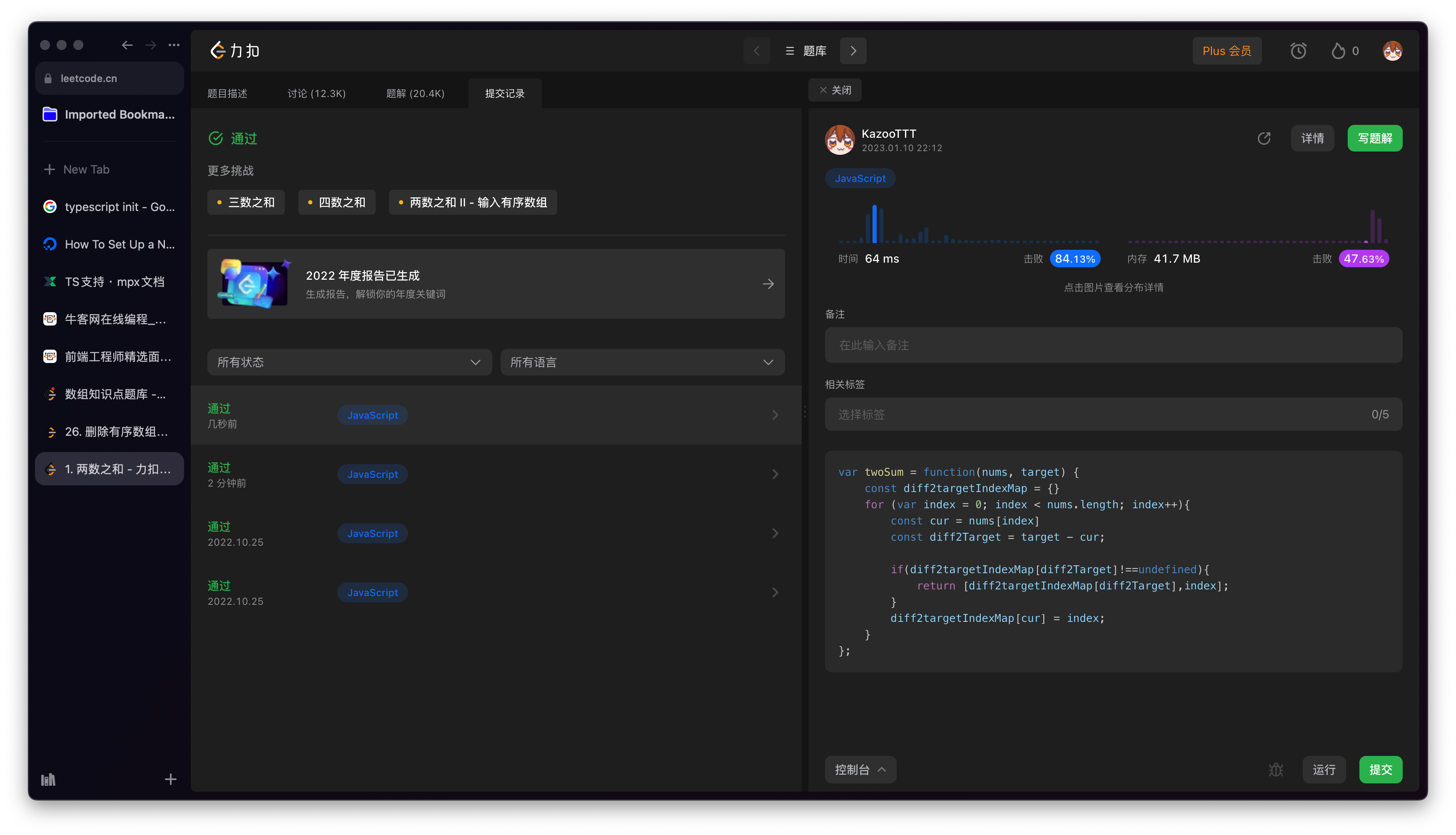
|
||||
|
||||
[26. 删除有序数组中的重复项 - 力扣(LeetCode)](https://leetcode.cn/problems/remove-duplicates-from-sorted-array/submissions/394407635/)
|
||||
使用的方法比较简单,性能比较差
|
||||
|
||||
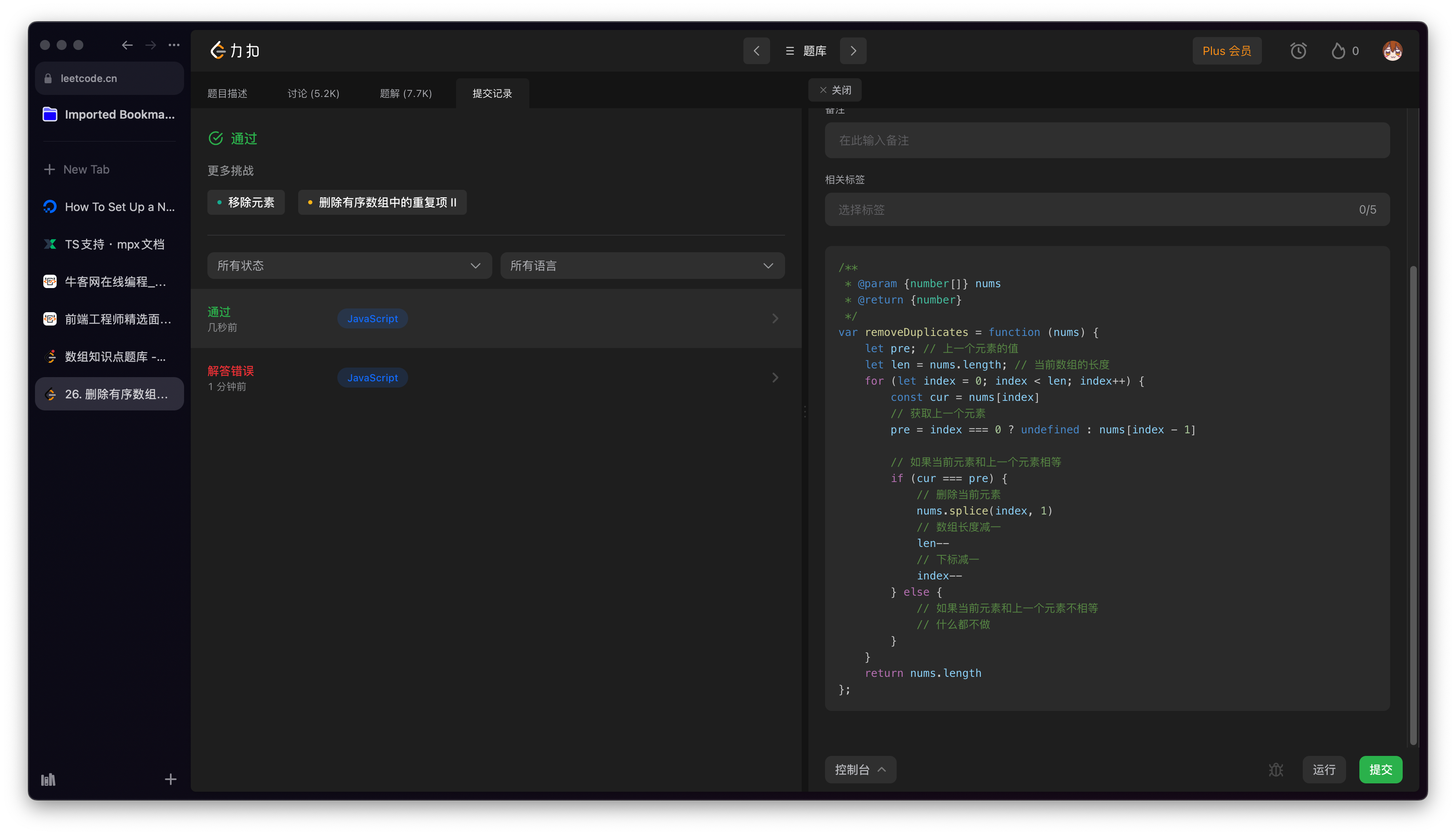
|
||||
|
||||
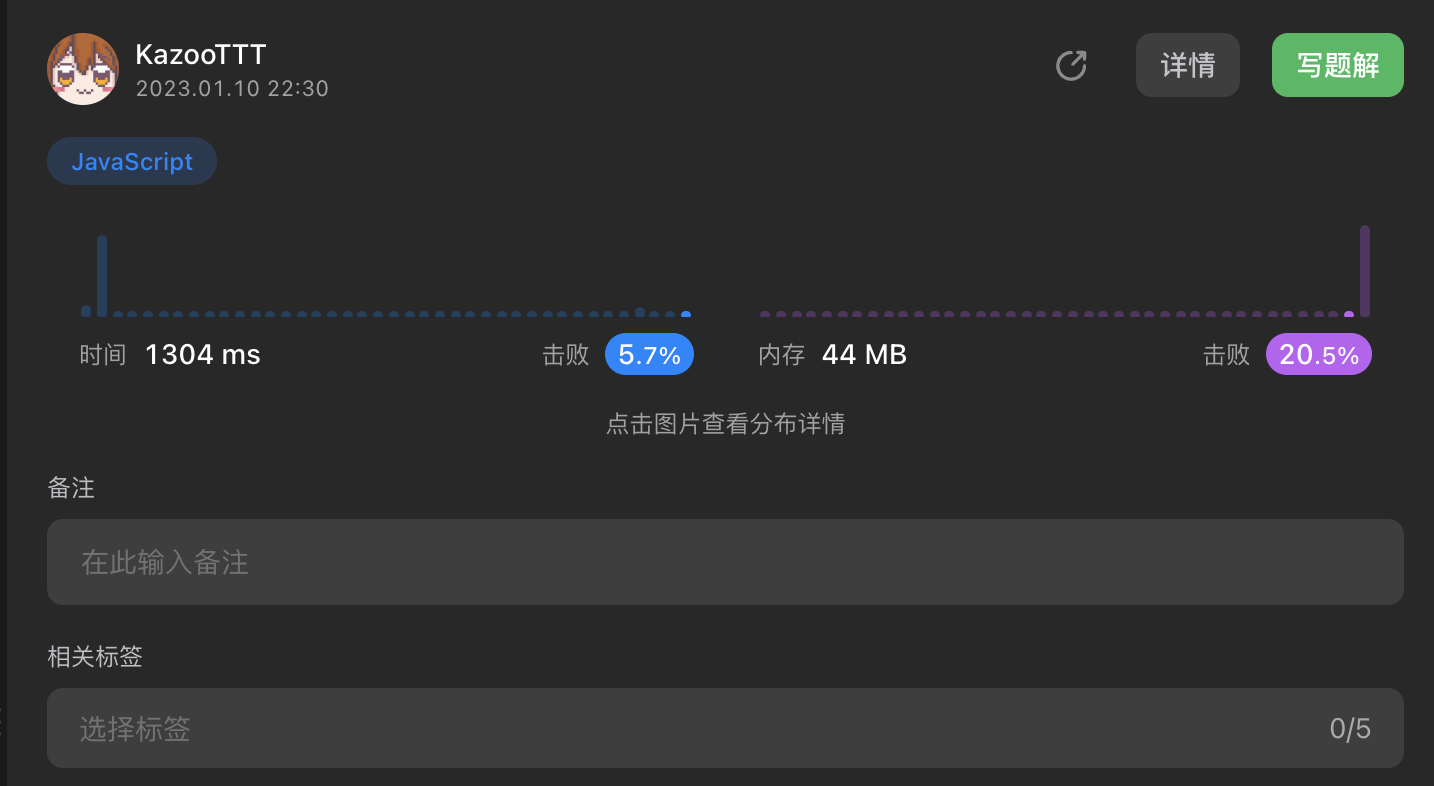
|
||||
|
||||
[27. 移除元素 - 力扣(LeetCode)](https://leetcode.cn/problems/remove-element/submissions/394409513/)
|
||||
|
||||
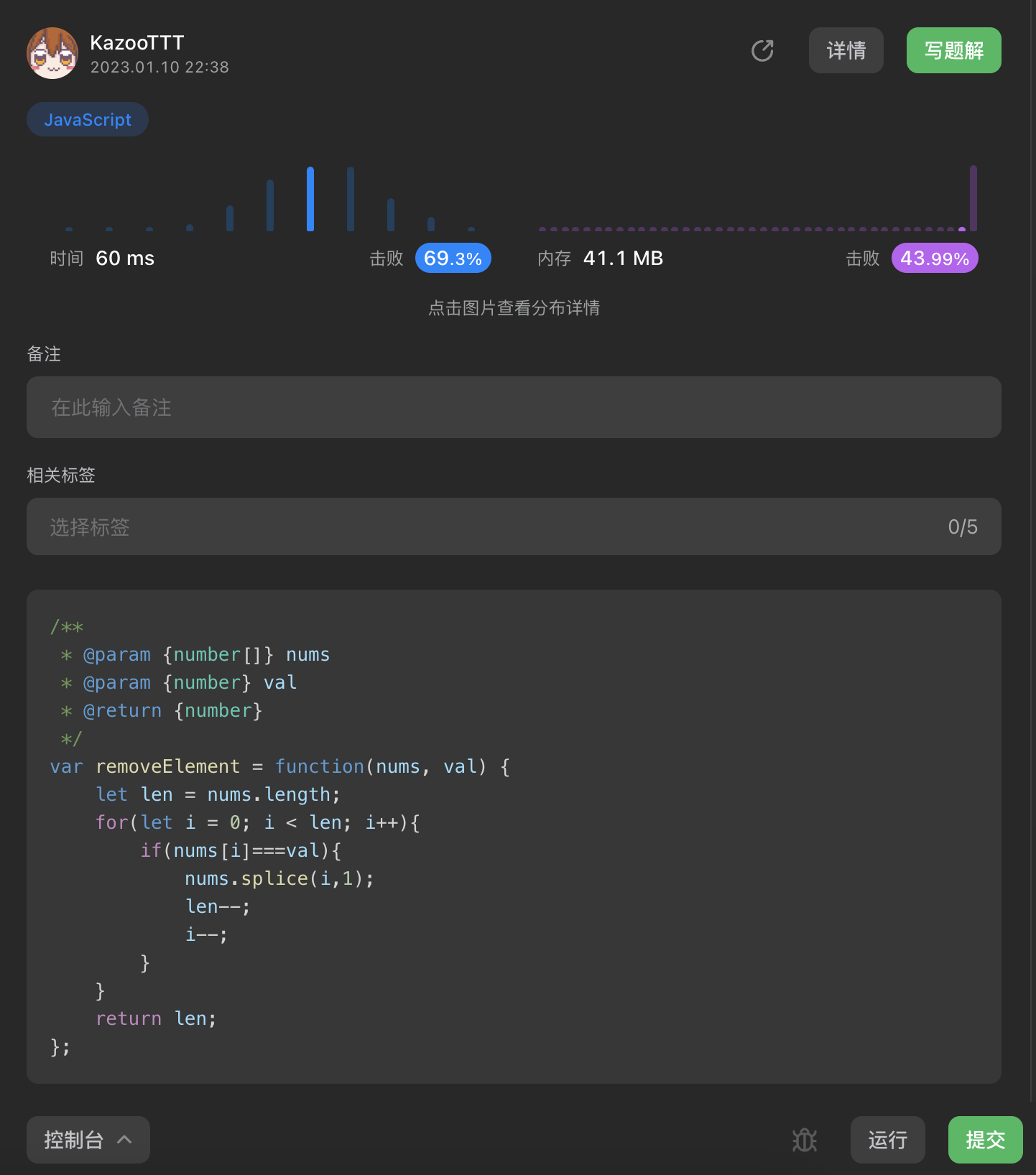
|
||||
Reference in New Issue
Block a user